CASE20210810_001
Clinical Effect Of Instantaneous Wave-Free Ratio On Recanalization Of A Patient With Moderate Obstruction Of Left Anterior Descending (LAD) And Chronic Total Occlusion (CTO) Of Right Coronary Artery (RCA)
By , , ,
Presenter
Ajith Prasanna Wanniarachchi
Authors
1, 1, 1, 1
Affiliation
, Sri Lanka1
Imaging - Physiologic Lesion Assessment
Clinical Effect Of Instantaneous Wave-Free Ratio On Recanalization Of A Patient With Moderate Obstruction Of Left Anterior Descending (LAD) And Chronic Total Occlusion (CTO) Of Right Coronary Artery (RCA)
1, 1, 1, 1
, Sri Lanka1
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
W.M.T.B
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 57-year old male who had a past medical history of transient complete heart block (CHB), ventricular tachycardia (VT)complicating an inferior STEMI was followed up after an episode of unstable angina. On admission his blood pressure was 140/64 mmHg, heart rate was 55 beats per minute in sinus rhythm, respiratory rate was 70 beats per minute, height was 158 cm and weight 65 Kg. There was no clinical evidence of pulmonary hypertension or heart failure.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Capillary blood sugar level was 108 mg/dl. Serum creatine level was 1 mg/dl. Serum electrolyte levels were within normal ranges. An echocardiogram demonstrated a moderate size ostium secundum ASD.
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Coronary angiogram demonstrated triple vessel disease with a CTO of the RCA, 40% stenosis at ostium of LAD, moderate (70%) stenosis in the proximal segment of the LAD artery and70% stenosis in the left circumflex artery.
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Patient has been initially referred for coronary artery bypass grafting and ASD surgical repair before physiological assessment. Physiological assessment of the LAD and LCX were undertaken. A Verrata plus Pressure guide wire was inserted into the LAD and pressures were equalized at the ostium of the LAD artery, and advanced distal to the stenosis. The iFR value was 0.94 indicating a non-flow limiting stenosis. iFR for the LCX demonstrated a value of 0.93 which again indicating a non flow-limiting stenosis. Therefore it was decided to perform a percutaneous coronary intervention for the CTO lesion of the RCA and to medically manage the LAD and LCX lesions. After the physiological coronary assessment, RCA CTO percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was performed successfully and a 2.25 mm x 28 mm Xience prime DES was implanted in the mid RCA, another 2.75 x 38 mm Xience prime DES was implanted in the mid to proximal RCA with an overlapping segment. ASD was also closed percutaneously with a 28mm size Cocoon R septal occluder device at the same time. Patient made an uneventful recovery and was discharged on the post-op day 2.
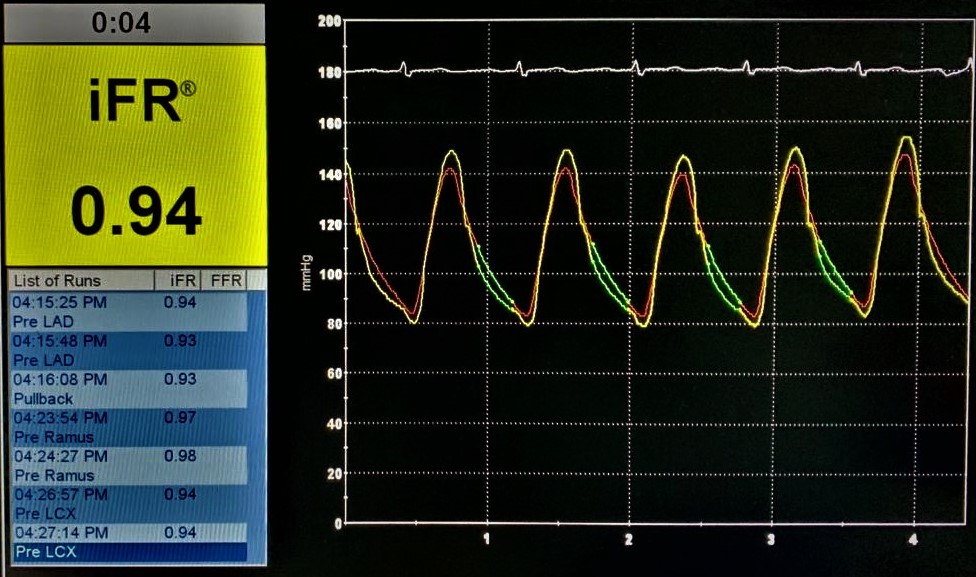
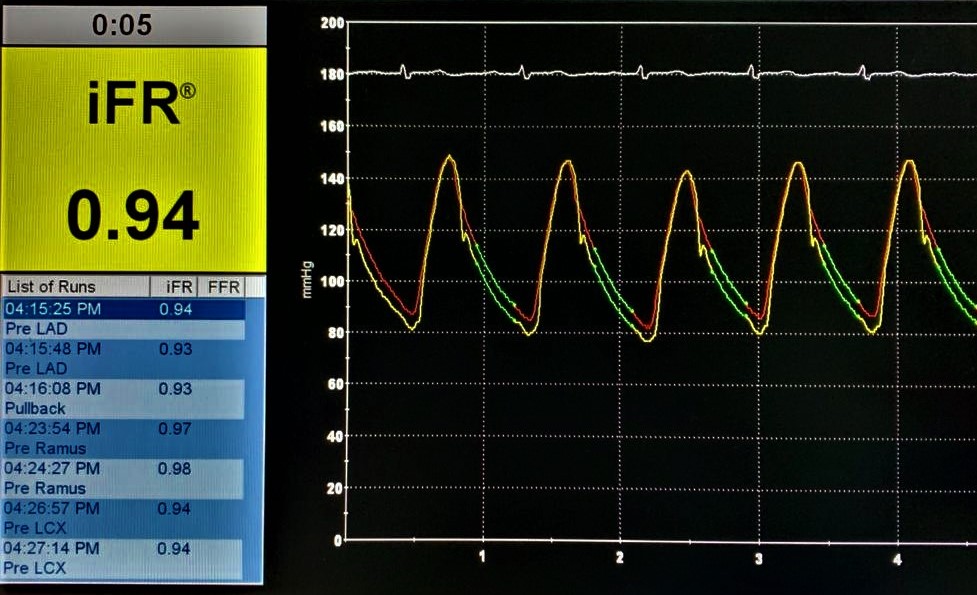


Case Summary
This case demonstrates the clinical effect of Physiological coronary artery assessment with the technique of iFR for intermediate coronary artery stenosis and it is useful in decision making of the management and prevent unnecessary surgical interventions such as CABG and surgery related stress and complications.
