CASE20210728_001
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction of a Single Coronary Artery Circulation
By , , ,
Presenter
Kristy Garganera
Authors
1, 1, 1, 1
Affiliation
, Philippines1
High-Risk Intervention (diabetes, heart failure, renal failure, shock, etc) - High-Risk Intervention
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction of a Single Coronary Artery Circulation
1, 1, 1, 1
, Philippines1
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
JR
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 59-year-old male hypertensive, smoker, presented with sudden onset angina and managed as a case of ST elevation MI in leads II, III, aVF given thrombolysis however there was still persistence of chest pain hence referred for rescue PCI. At the ER his vital signs are as follows BP 140/80, CR 74 bpm, RR 21 cpm, T 37.2'C. Pink palpebral conjunctiva, non-engorged neck veins, clear breath sounds, apex beat displaced at the 5th intercostal space anterior axillary line with no murmur, good pulses.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
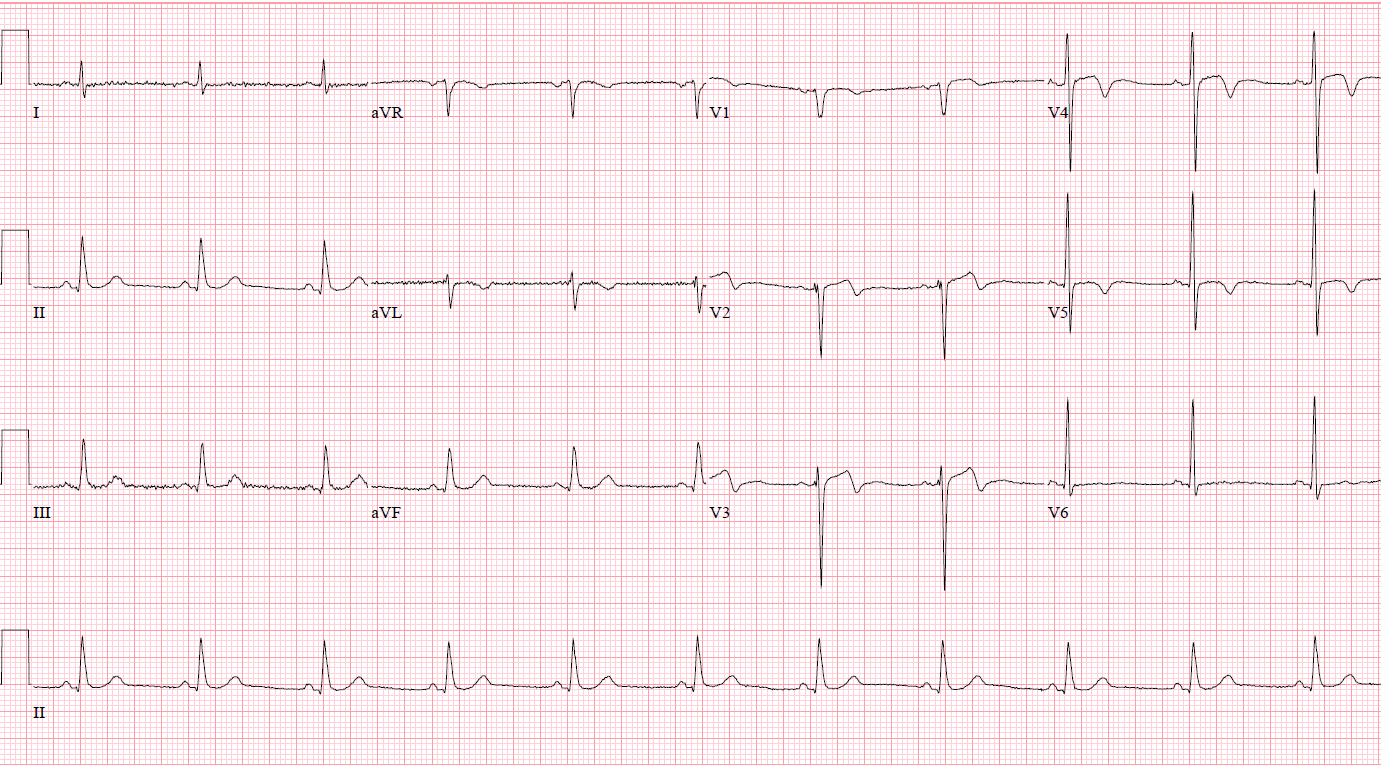
12-lead ECG showed normal sinus rhythm with T wave abnormalities leads V2 - V5. Chest X-ray showed atherosclerotic aorta with mild degenerative osseous changes. HS Troponin I at 52270 pg/mL, total cholesterol was 4.50 mmol/L, HDL 1.04 mmol/L, LDL 2.62 mmol/L, triglyceride 2.69 mmol/L. A 2D echocardiogram showing a concentric LV remodeling with hypokinesia of the anteroseptal wall and EF of 45.1% by Simpsons biplane, grade 1 LV dysfunction, aortic sclerosis with mild aortic regurgitation.

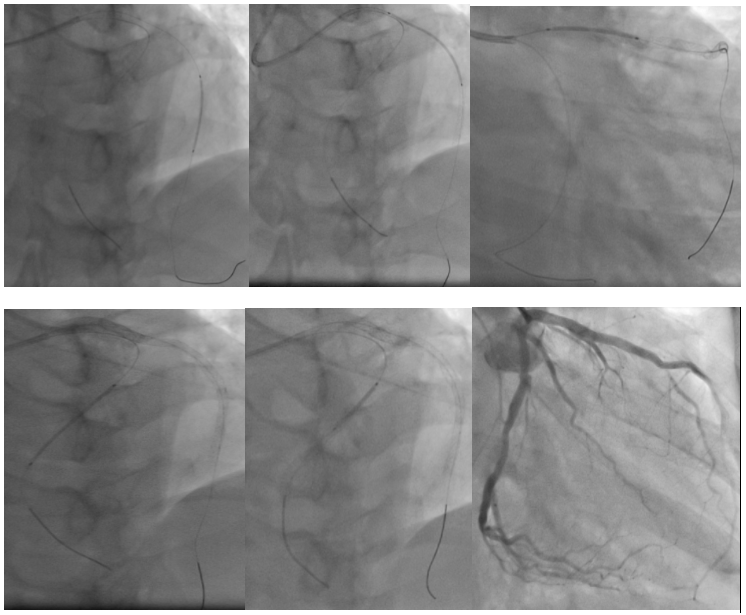
Relevant Catheterization Findings
LMCA is a 5mm short vessel that bifurcates into the LAD and LCx. The LAD is a 3.5mm type III diffusely diseased vessel at its proximal to mid segments with worst stenosis of 95%. LCx is a 3.5mm diffusely diseased vessel with worst stenosis of 70% at its mid segment. OM branches are good-sized branching vessels. LPDA is a 1.0mm vessel. An absent RCA was confirmed by doing an aortogram via hand injection. IVUS show mixed plaque in lesion areas with LAD MLA 3.80mm2 and LCx MLA 3.18mm2.
 JR CA video.avi
JR CA video.avi
 JR Aortogram.avi
JR Aortogram.avi
 JR CA video 2.avi
JR CA video 2.avi
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
IVUS-guided PCI of LAD and LCx was done using a 6F XB 3.5 mm guide catheter. A coronary wire was distalized to the LAD and another coronary wire distalized to the LPDA. Post dilation of mid to proximal LAD target lesions done using 2.0x20 mm balloon catheter at 12-16 ATM. A DES 2.5x26 mm positioned at the mid LAD and deployed at 12 ATM, followed by deployment of the second DES 3.0x38 mm at the proximal to mid LAD with 2 mm distal overlap at 12 ATM. A third DES 3.5x22 mm was positioned at the proximal LAD with 1-2 mm distal overlap from the second stent and deployed at 14 ATM. Next, predilation of LCx target lesion using 2.0x20 mm balloon catheter positioned at the distal LCx and inflated at 7 ATM. A DES 2.75x30 mm was positioned at the distal LCx and deployed at 14 ATM. A second DES 3.0x15 mm was positioned at the mid LCx with a 1-2 mm distal overlap from the first stent and deployed at 14 ATM. Post dilation done using the same 3.0x15 mm stent balloon positioned at the junction of the first and second stents of the LCx and inflated at 16 ATM. IVUS done revealing complete stent apposition to the vessel walls with the following measurements: LAD MSA of 6.65 mm2, LCx MSA of 5.42 mm2, plaque burden of <50% in the distal landing areas, with no edge dissection. Post PCI angiography of the LAD and LCx revealed a TIMI 3 flow with no residual stenosis and perforation.
 JR postPCI.avi
JR postPCI.avi
 JR post-PCI angiography.avi
JR post-PCI angiography.avi

Case Summary
An aggressive approach in the management of a single coronary artery, in this particular patient - an absent right coronary artery, is important because of the risk of sudden cardiac death when the only existing coronary circulation becomes compromised such as an acute coronary occlusion. Thus, as done in this case, an intravascular ultrasound-guided percutaneous coronary intervention with stenting was done to treat the coronary obstruction.
