CASE20240816_013
"Young" STEMI in Coronary Artery Aneurysms
By Bu-Yuan Hsiao, Ping-Ping Wang
Presenter
Ping-Ping Wang
Authors
Bu-Yuan Hsiao1, Ping-Ping Wang1
Affiliation
Taipei Medical University Hospital, Taiwan1,
View Study Report
CASE20240816_013
ACS/AMI - ACS/AMI
"Young" STEMI in Coronary Artery Aneurysms
Bu-Yuan Hsiao1, Ping-Ping Wang1
Taipei Medical University Hospital, Taiwan1,
Clinical Information
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
Mr. Kao, is a 28-year-old male, and has no systemic diseases before. He suffered from intermittent chest tightness and dyspnea for 3 days.The symptoms got worse when walking, and relieved after rest.
There is no associated family history.

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
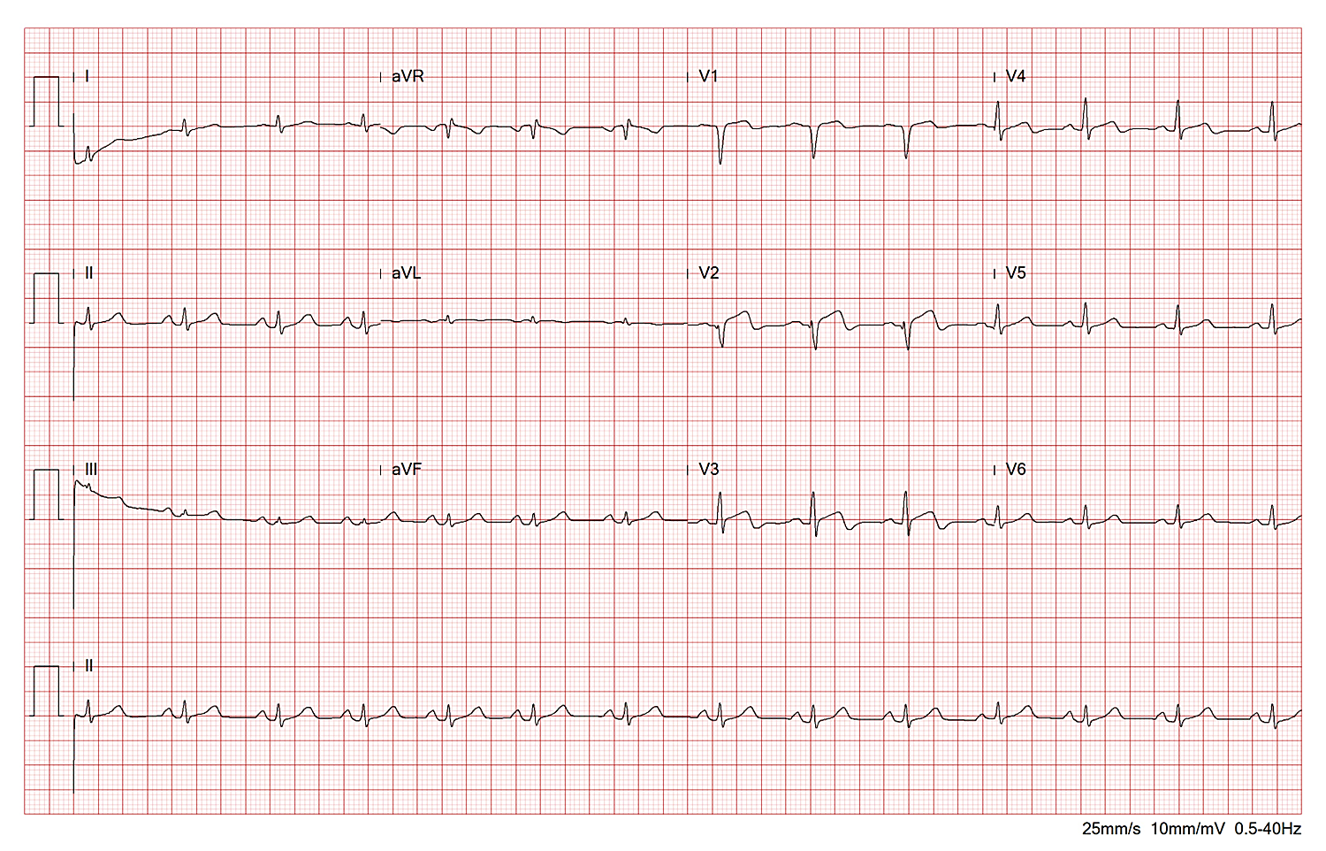
ECG showed Sinus rhythm, and biphasic T wave in precordial leads.The lab data: CPK= 351 U/L, CK-MB= 30 U/L, Troponin-I= 0.447 ng/ml. NT-pro BNP= 1033 pg/ml.

Relevant Catheterization Findings
CAG showed(1) LM: Aneurysm.(2) LAD: Aneurysm in the proximal part, then critical lesion the middle part.(3) Ramus: Aneurysm.(4) LCx: Ectasia.(5) RCA: Aneurysm in the Orifice, and then total occlusion, only collateral circulations to distal RCA.
 LAD.mp4
LAD.mp4
 LCx.mp4
LCx.mp4
 RCA.mp4
RCA.mp4
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
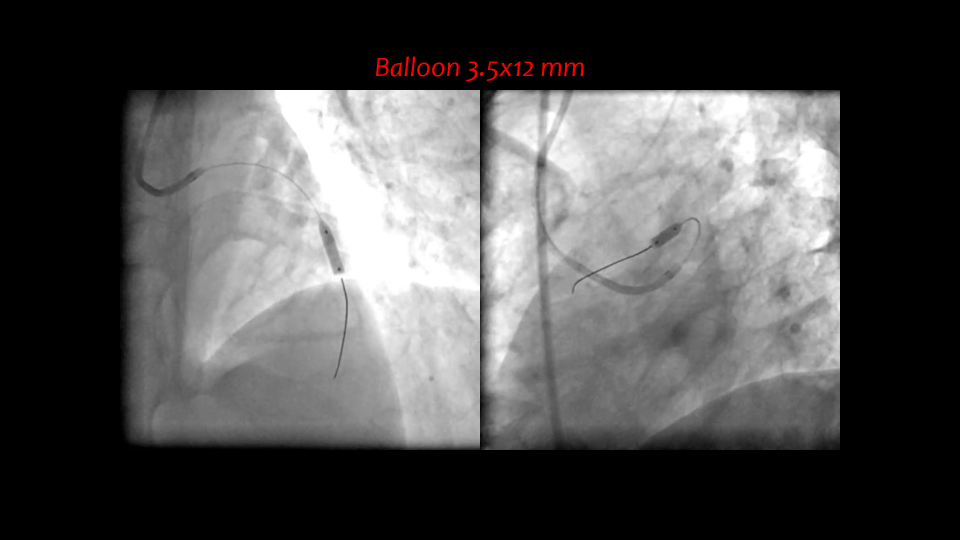
Initially we dilated the critical lesion with balloon 2.0x15 mm in the left anterior descending artery.Then we used IVUS to evaluate the left anterior descending artery, and it revealed aneurysm diameter around 5.0~7.0 mm.We predilated with balloon 3.5x12 mm.Afterward, we deployed a drug-eluting stent 3.5x16 mm.The we performed post-dilatation with non-compliant balloon 5.0x8 mm after IVUS evaluation of the the proximal aneurysm size.The final coronary angiogram showed good stent apposition and distal flow.
 Final.mp4
Final.mp4
 Final (2).mp4
Final (2).mp4

Case Summary
(1) Clinical presentations of coronary artery ectasia (CAE) vary widely, from asymptomatic cases to high-risk ACS. (2) Treatment should be personalized on the basis of the location, size, and morphology of coronary artery aneurysms (CAAs); the presence of thrombi; and the clinical characteristics of patients. (3) The optimal treatment approach remains to be identified.
