CASE20240816_004
Imaging-Guided Rota/IVL for Complex Calcified Plaque Treatment — Eccentric and Calcified Nodule: The Rota Sniper Method
By Hsin-I Teng
Presenter
Hsin-I Teng
Authors
Hsin-I Teng1
Affiliation
Cheng Hsin General Hospital, Taiwan1,
View Study Report
CASE20240816_004
DES/BRS/DCB - DES/BRS/DCB
Imaging-Guided Rota/IVL for Complex Calcified Plaque Treatment — Eccentric and Calcified Nodule: The Rota Sniper Method
Hsin-I Teng1
Cheng Hsin General Hospital, Taiwan1,
Clinical Information
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
The patient is a 69-year-old male with a history of coronary artery disease, presenting with intermittent chest tightness and shortness of breath during exercise. The patient has been diagnosed with significant calcified plaque in the right coronary artery (RCA), particularly in segments 1 and 2. The calcification is described as thick, eccentric, and challenging, contributing to difficulties with stent deployment in prior interventions.
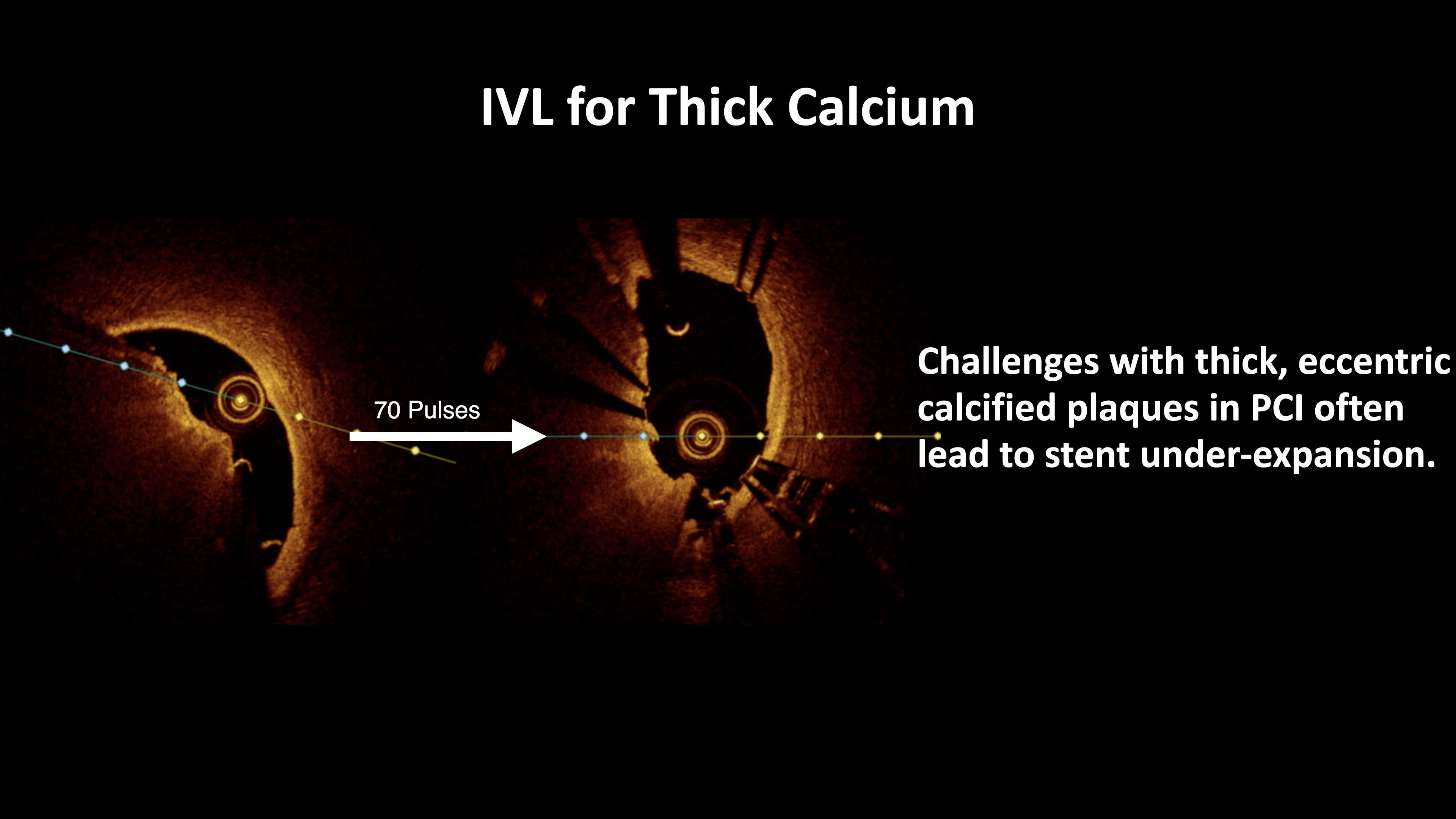
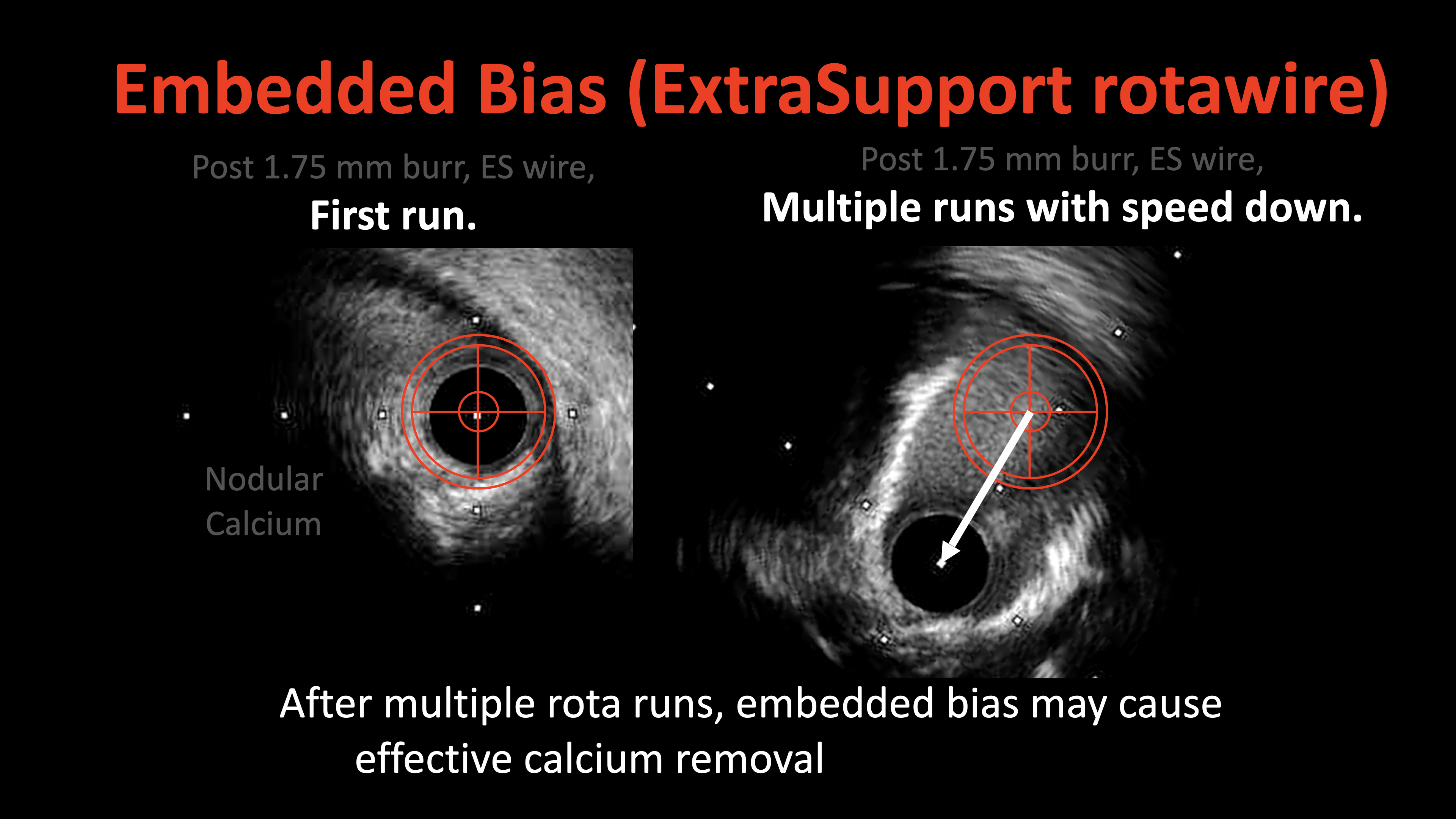
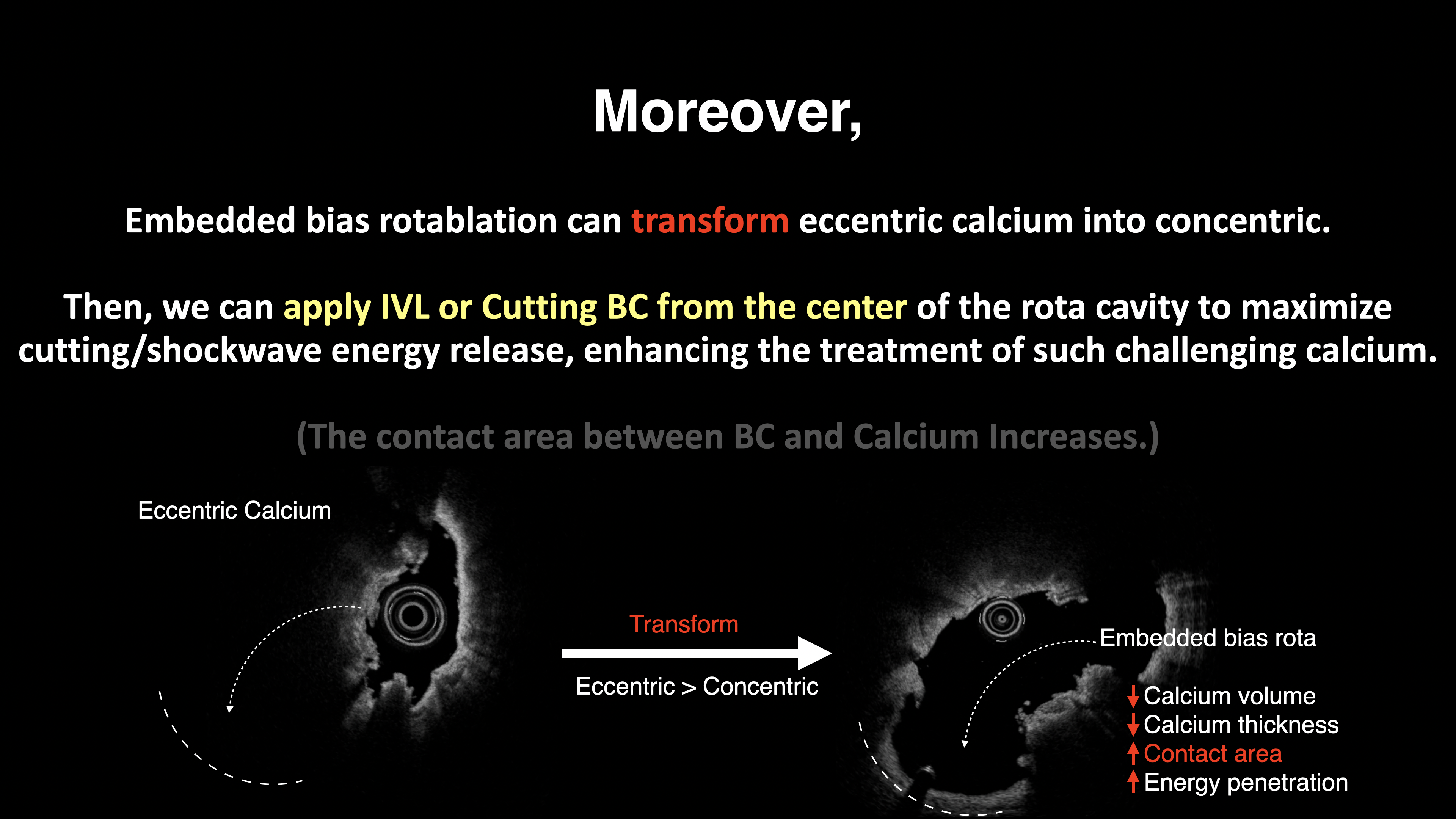



Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
NIl
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Calcified plaque located in the right coronary artery (RCA), particularly in segments 1 and 2. The calcification is described as thick, eccentric, and challenging, contributing to difficulties with stent deployment in prior interventions.
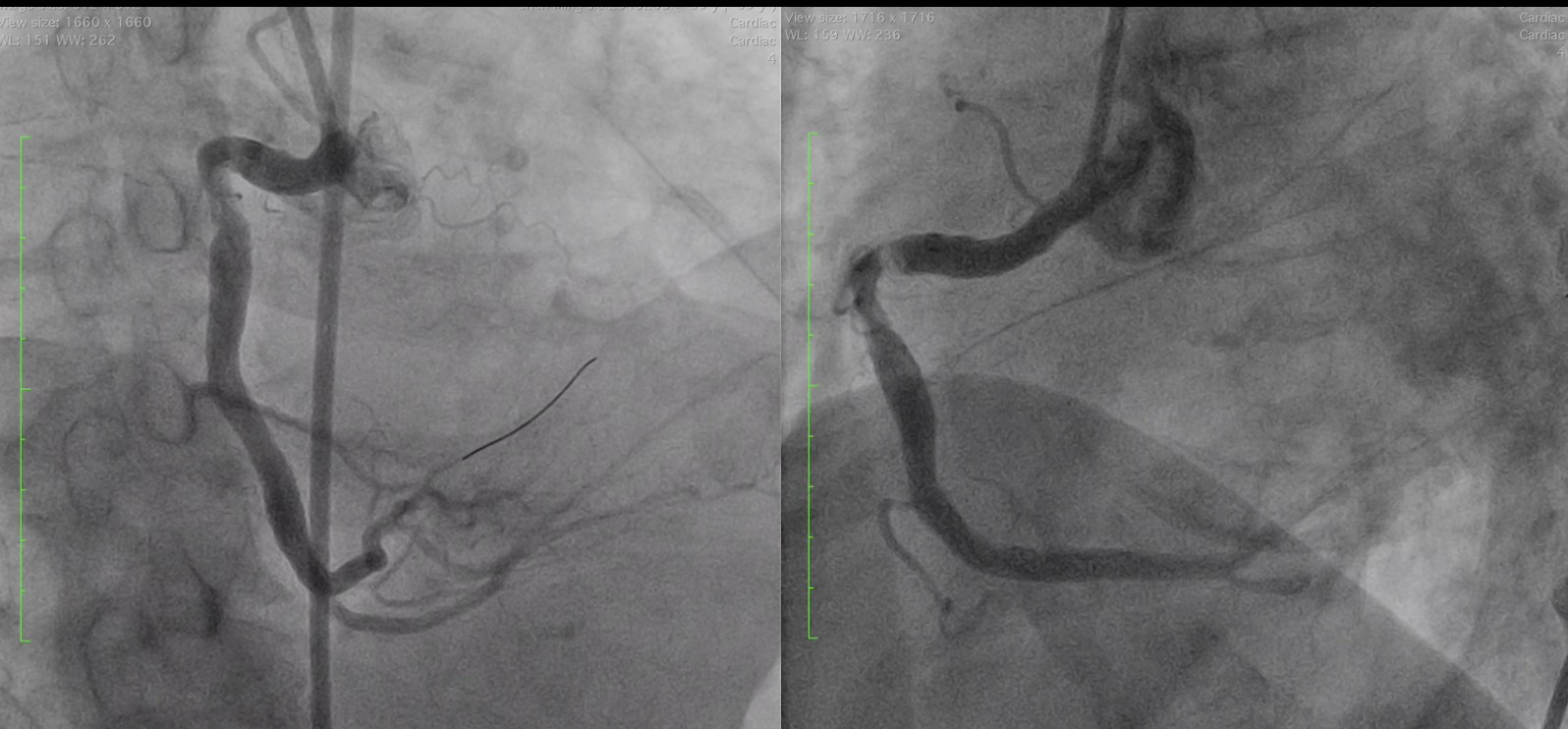

Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Given the complex nature of the calcified plaques, the patient underwent imaging-guided intravascular lithotripsy (IVL) following multiple rotablation runs. The first rotablation was performed with a 1.75 mm burr at 180,000 to 140,000 rpm, using an ExtraSupport wire and speed-down technique to ensure safety and effectiveness. However, due to the thick and eccentric nature of the calcified plaque, additional rotablation with a 2.15 mm burr at 160,000 rpm was required, followed by IVL with a 4.0 mm balloon to optimize lesion preparation from the center of rota-cavity to release the energy of shockwave fully. This newly developed Rota-Sniper technique ensures the best round-shaped stent expansion in such challenging calcified plaques in the current PCI era.
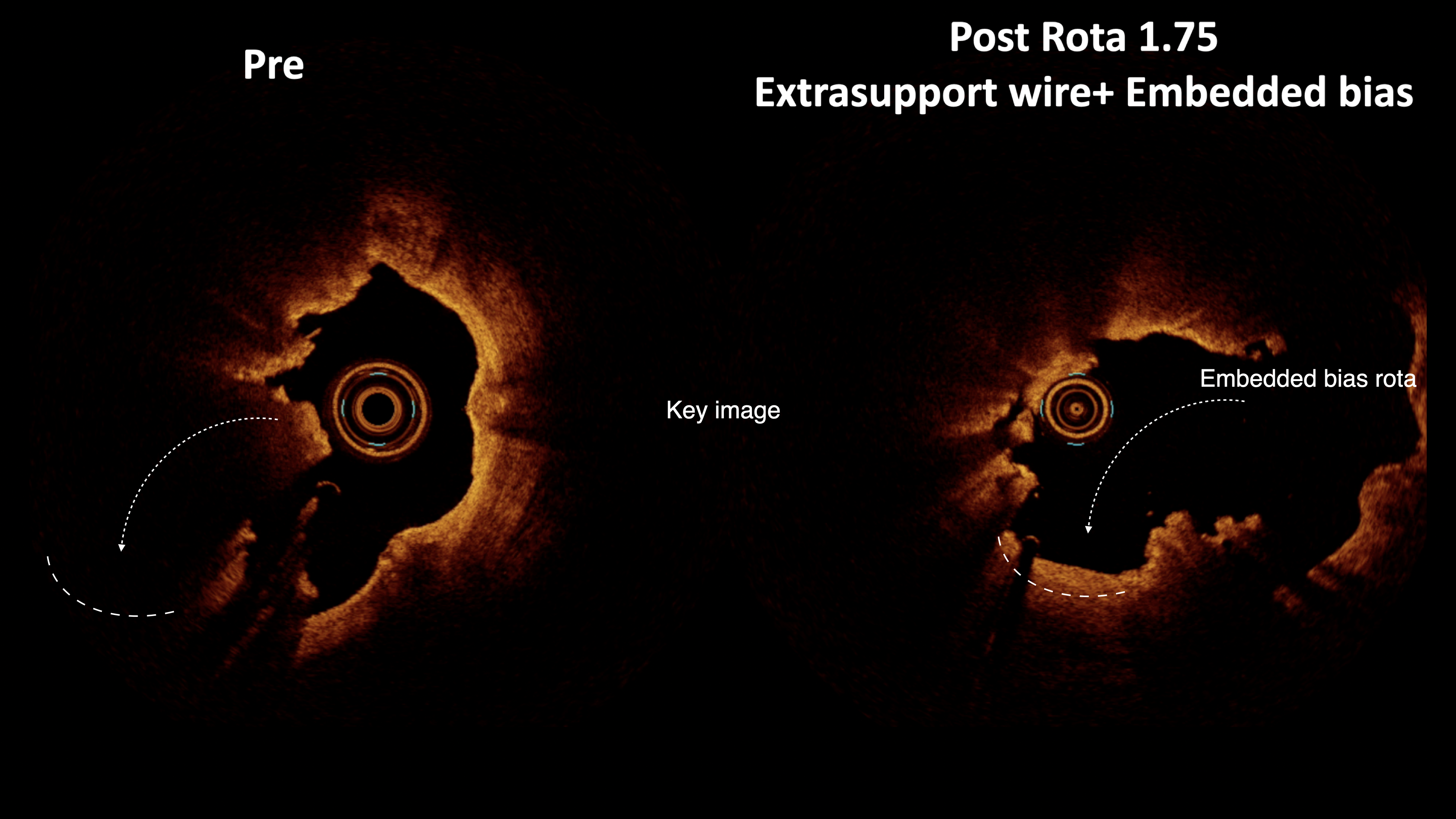
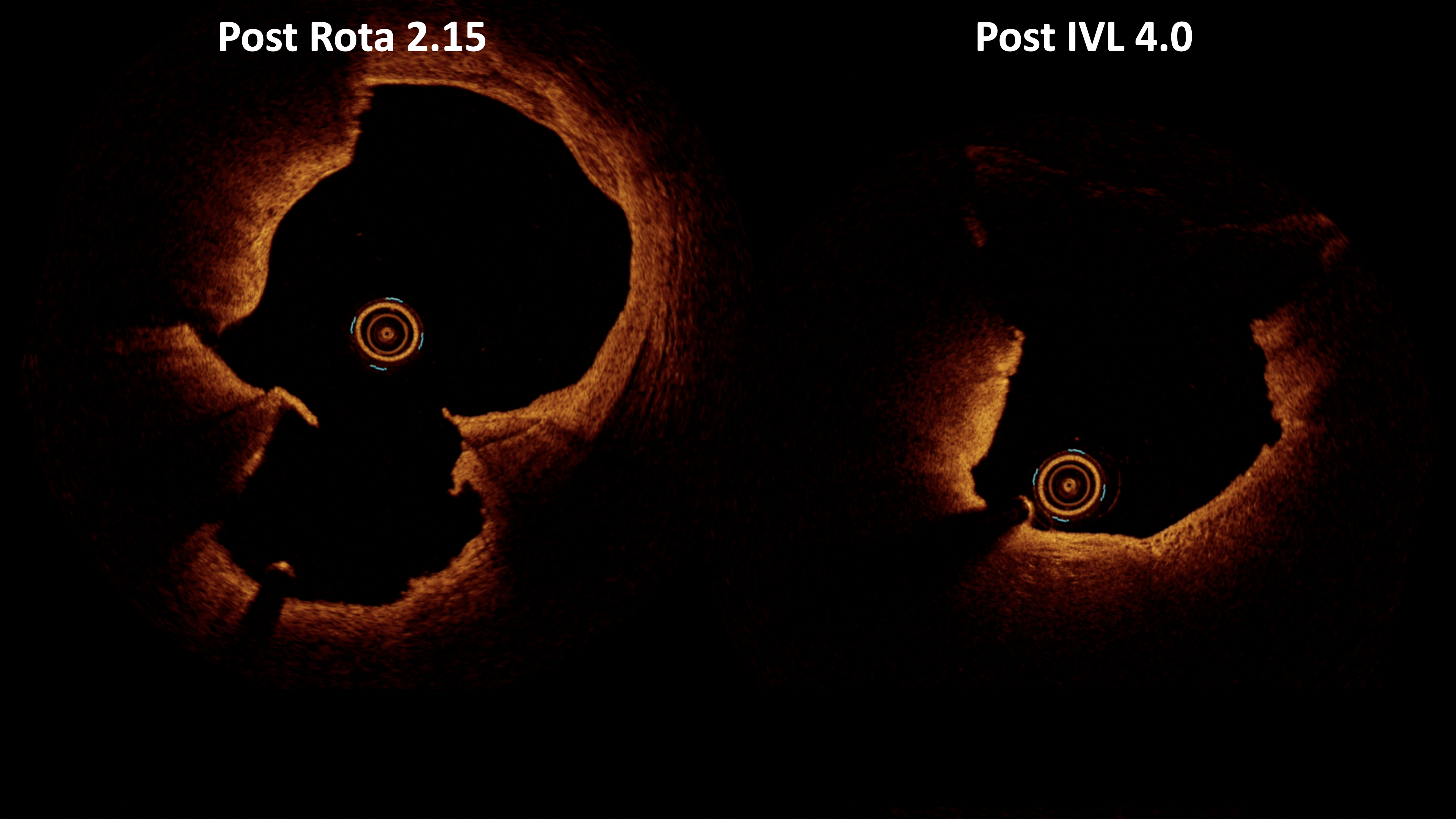
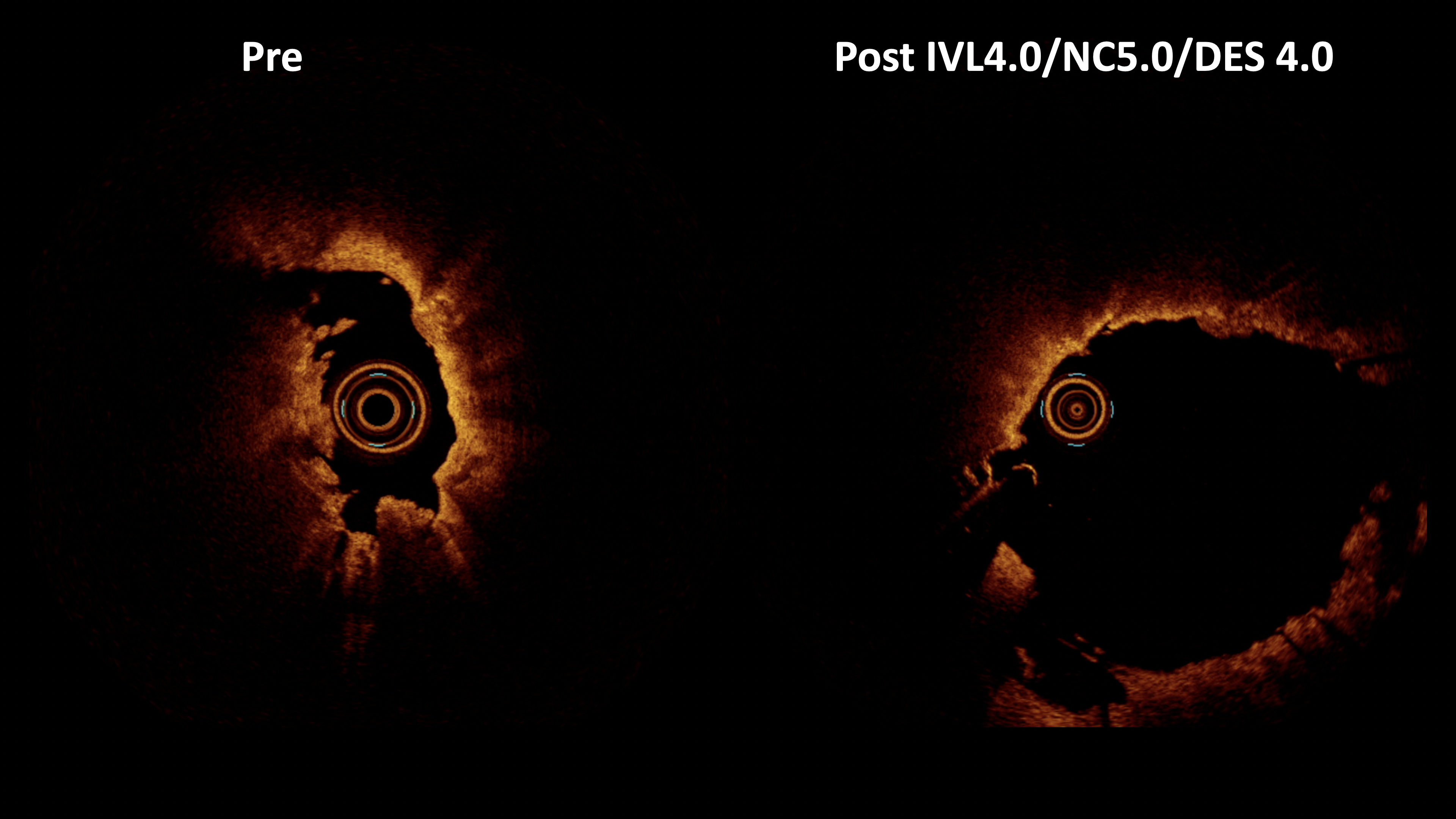



Case Summary
The main purpose of the RotaSniper technique is safety. Position a virtual circle over the rotawire in our mind and check whether this circle will touch the media by imaging. In this way, there might be no more perforation during rotablation. RotaSniper, which can further combine debulking area prediction and embedded wire bias, enables a horizontal rotablation path against challenging calcified plaques. Transforming eccentric calcium into concentric and softening residual calcium with lithotripsy or cutting BC ensures optimal stent expansion and better long-term outcomes.
