CASE20240731_001
Hybrid Approach of Photon-counting Computed Tomography and Intravascular Ultrasound for Chest Pain: A Case Report of Successful Management and 6-Month Follow Up
By Duc Chinh Nguyen, Duong Quoc Anh Nguyen, Duong Khang Nguyen, Chi Cuong Tran, Huong Thi Quynh Tran
Presenter
Huong Thi Quynh Tran
Authors
Duc Chinh Nguyen1, Duong Quoc Anh Nguyen1, Duong Khang Nguyen2, Chi Cuong Tran1, Huong Thi Quynh Tran3
Affiliation
Can Tho Stroke International Services General Hospital, Vietnam1, School of Population Health, Curtin University, Australia2, The International Hospital S.I.S, Vietnam3,
View Study Report
CASE20240731_001
Imaging & Physiology - Non-Invasive Imaging (CTA, MRI, Echo, etc)
Hybrid Approach of Photon-counting Computed Tomography and Intravascular Ultrasound for Chest Pain: A Case Report of Successful Management and 6-Month Follow Up
Duc Chinh Nguyen1, Duong Quoc Anh Nguyen1, Duong Khang Nguyen2, Chi Cuong Tran1, Huong Thi Quynh Tran3
Can Tho Stroke International Services General Hospital, Vietnam1, School of Population Health, Curtin University, Australia2, The International Hospital S.I.S, Vietnam3,
Clinical Information
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
This is a case of a 47-year-old female patient with a history of hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Shepresented after a 3-week course of typical angina episodes. She was then treated with clopidogrel, rosuvastatin, isosorbide mononitrate, metoprolol and trimetazidine. After 17 days, she still experienced typical chest pain at exertion. This led to her hospitalization. Vital signs at admission were within normal range.

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
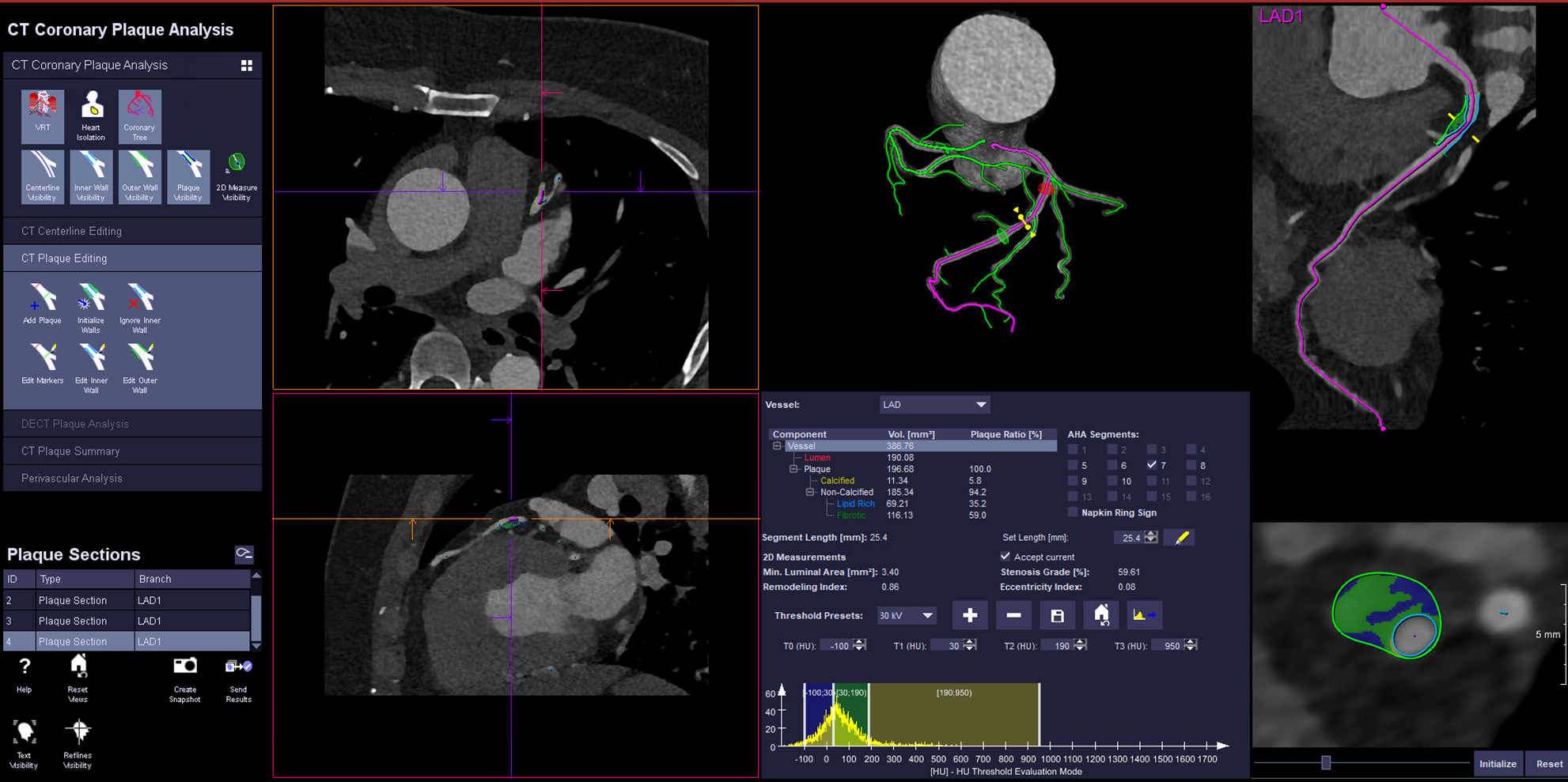
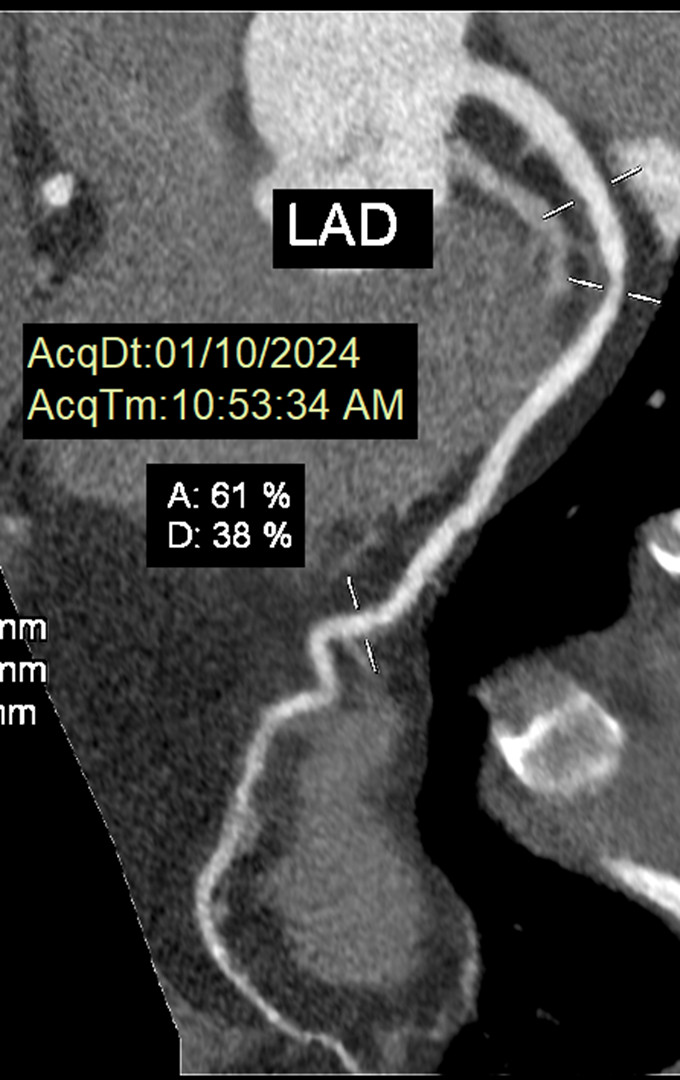
Electrocardiogram was not significant and troponin concentratin was not elevated. eGFR was 87.13 mL/min/1.73 m2, NT-proBNP was 59.6 pg/mL. The photon-counting computed tomography at the time showed 59.61 % stenosis of proximal left anterior descending artery with a lipid volume of 69.2 mm2, correlated to 35.2 % of lipid core burden.

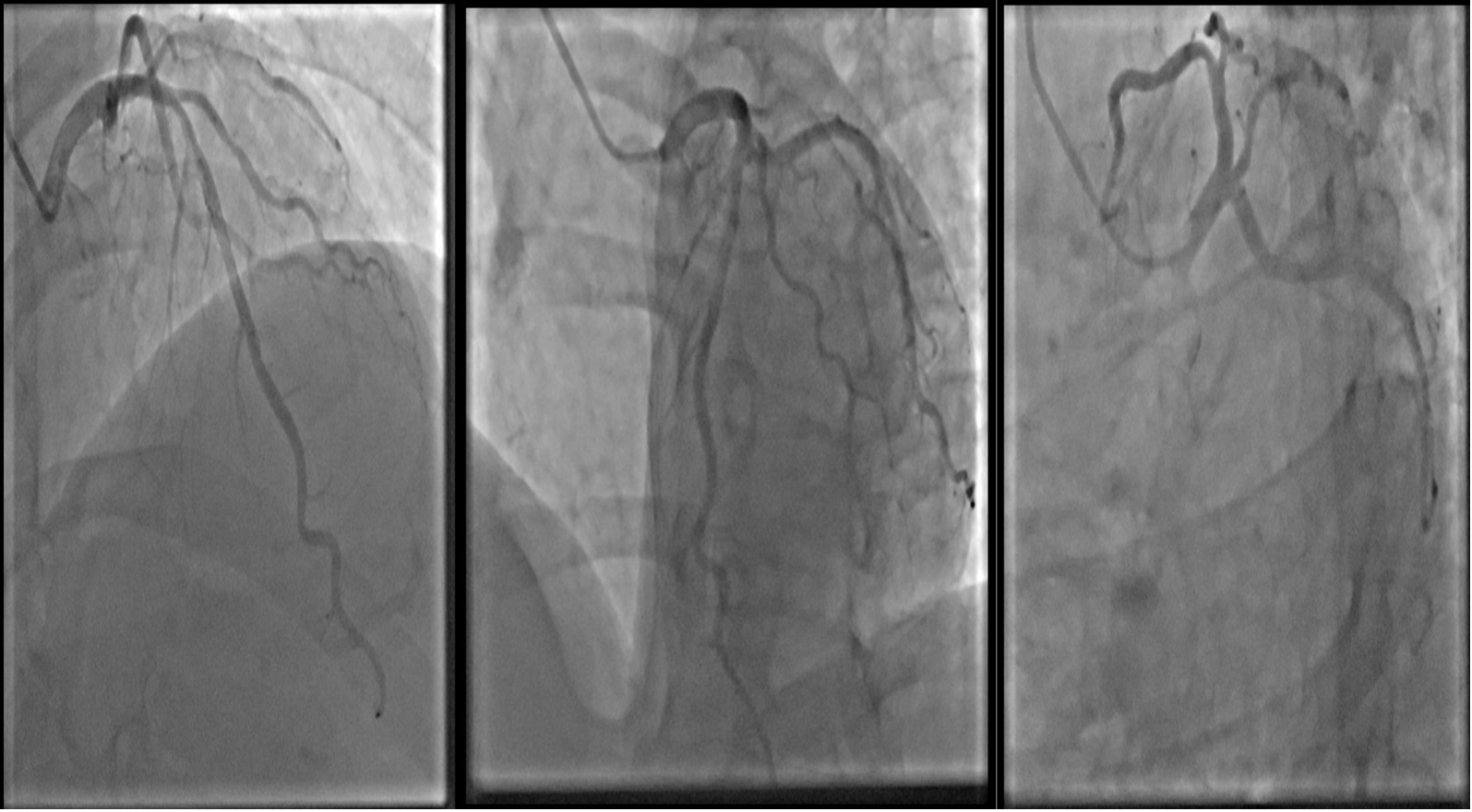
Relevant Catheterization Findings
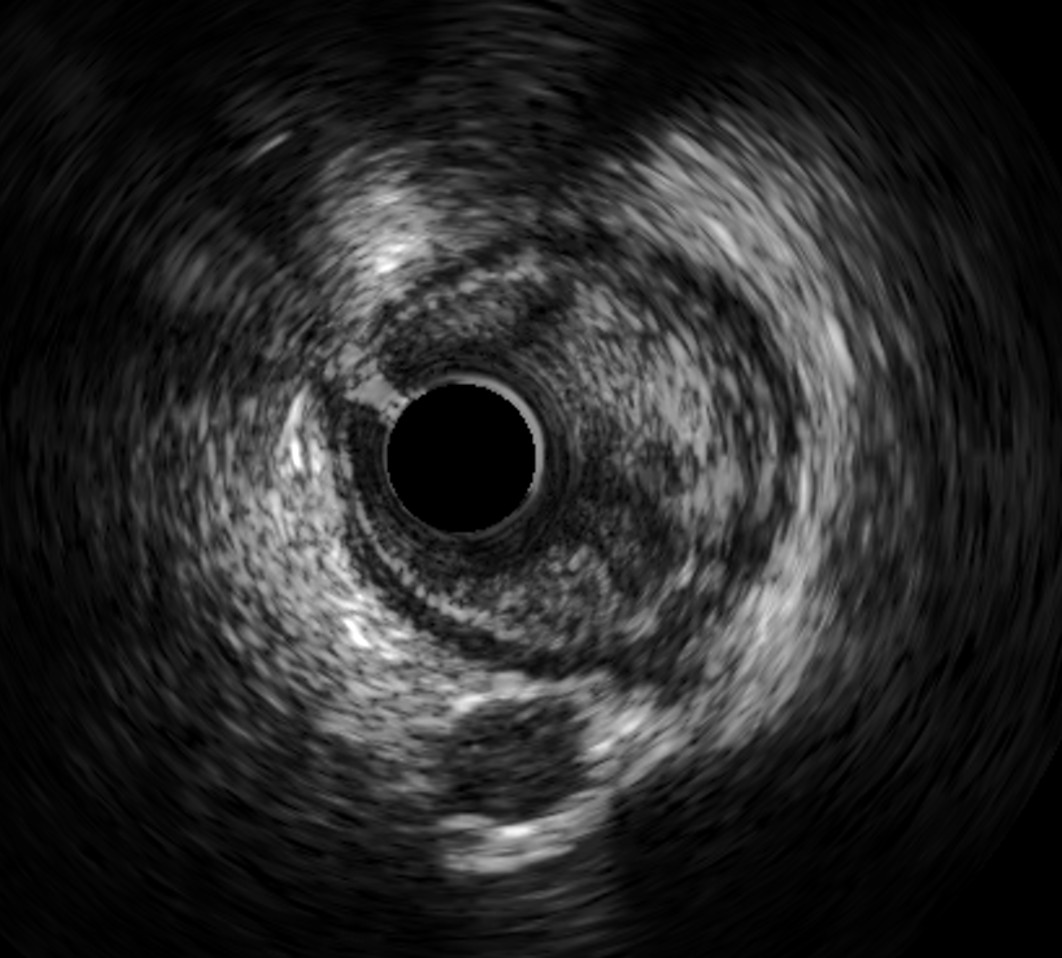
Coronary angiography showed 70 % stenosis and suspected ulceration of promximal left anterior descending artery (LAD), myocardial brigde caused 40 % stenosis of LAD II, with 40 % stenosis of mid-left circumflex artery and 30 % stenosis of mid-right coronary artery. Intravascular ultrasound showed plaque ulceration in proximal LAD with minimum lesion area of 2.6 mm2, proximal reference diameter of 3.7 mm, distal reference diameter of 3.2 mm and plaque burden of 76 %.


Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Intravascular ultrasound showed plaque ulceration in proximal LAD with minimum lesion area of 2.6 mm2, proximal reference diameter of 3.7 mm, distal reference diameter of 3.2 mm and plaque burden of 76 %. The intervention decision was made based on two indications: chest pain refractory to medical treatment, and high-risk unstable atherosclerosis on intravascular ultrasound. A 3.0 x 28 mm drug-eluting stent was employed, and intravascular ultrasound was conducted after intervention to ensure optimal intervention, which revealed no egde dissection, minimum stent area was 7.4 mm2 and was 92 % of distal lumen reference. She was then discharged after an uneventful hospital stay. 6-month follow up showed absence of angina with improvement in physical health.
 IVUS PRE PCI.mp4
IVUS PRE PCI.mp4
 IVUS POST PCI.mp4
IVUS POST PCI.mp4

Case Summary
Combination of photon-counting computed tomography and intravascular ultrasound is new and promising. Early detection of unstable lesions in photon-counting computed tomography and proceed to intravascular ultrasound-based coronary intervention can improve diagnosis accuracy and bring optimal results to both procedural and clinical prospects.
